Airborne Measurements of Spectrally Resolved Actinic Flux and Photolysis Frequencies:
Instrumentation description
Richard E. Shetter and Christopher A. Cantrell
Atmospheric Chemistry Division, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
Spectrally resolved actinic flux measurements from 290-420 nm and
atmospheric photolysis frequency measurements will be provided on the NASA
DC-8 and P3-B aircraft for the PEM-Tropics B mission using actinic flux
spectroradiometry [Shetter and Muller, 1998]. The technique is based on
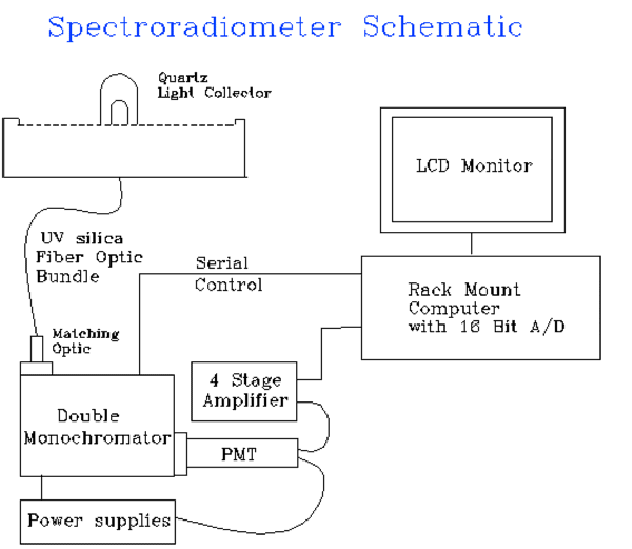
hemispherical quartz light collectors, double monochromators, and low dark
current photomultipliers. The instrument is represented schematically in
Figure 1.
Figure 1.

The instrument package on each aircraft will be identical and include 2 independent spectroradiometer systems. Since an individual spectroradiometer system collects the 2p steradian hemisphere above or below the aircraft, addition of the actinic fluxes will give the spherically integrated actinic flux. The instruments will have response and detection characteristics represented in Table 1.
|
Measurement |
Detection Limit |
Time Response |
Accuracy |
Precision |
|
Actinic Flux 280-420nm |
<0.05m W/cm2/nm |
<15 sec |
~10% |
~5% |
|
JO(1D) |
1x10-8 sec-1 |
<15 sec |
~10% |
~5% |
|
J(NO2) |
3x10-8 sce-1 |
<15 sec |
~10% |
~5% |