Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry-Based
Measurements of HO2 and RO2
Christopher A. Cantrell, NCAR Boulder, CO
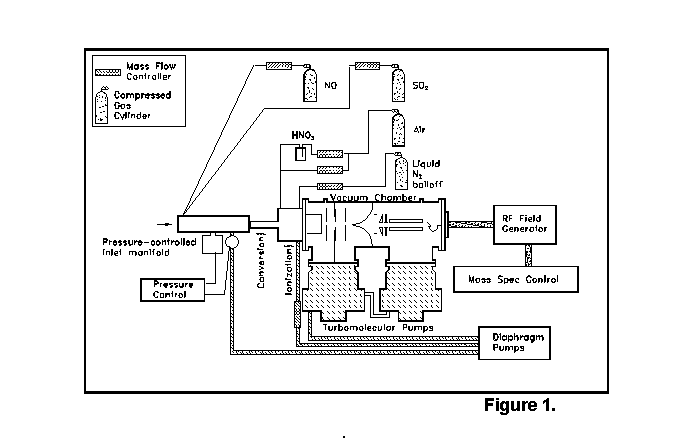
The peroxy radical CIMS (PerCIMS) is generally based on the selected ion CIMS measurement of hydroxyl radicals.In the PerCIMS method, reagent gases NO and SO2 are added to ambient air, leading to the conversion of ambient peroxy radicals (RO2 and/or HO2) to gas-phase sulfuric acid. The H2SO4 product is detected first by ionization through a proton transfer reaction with NO3-, followed by introduction into a vacuum system with ion optics, differential pumping, quadrupole mass filter and channel electron multiplier for ion counting. A schematic diagram of the instrument is shown below.
The PerCIMS instrument is unique in that we have developed methods to yield measurement of total peroxy radical levels ([HO2] + [RO2]), and measurement of [HO2] by adjusting the reagent gas concentrations in the inlet region. These two measurements together yield additional information about atmospheric processing of hydrocarbons and the branched chain reactions that lead to partitioning of peroxy radicals between the hydro- and organic-peroxy radical forms.
Calibration of the instrument is accomplished through photolysis of water vapor using 184.9 nm radiation from a low-pressure mercury lamp. Radical concentrations in the range of ambient concentrations (and higher) are easily generated by adjusting the lamp distance, slit width and water vapor concentration. The lamp flux is determined through N2O actinometry. Relative sensitivity of various peroxy radicals are measured using the photolysis of Cl2 to yield chlorine atoms that react with hydrogen and various hydrocarbon precursors.
These measurements are accomplished with an estimated ±30%
accuracy, typical detection limits of 1 x 107 radicals-cm-3
in 15 seconds, and typical 2
![]() precision of 10% at 1 x 108 radicals-cm-3.
Lower detection limits with better precision are possible with
appropriate averaging.
precision of 10% at 1 x 108 radicals-cm-3.
Lower detection limits with better precision are possible with
appropriate averaging.